- How to read EKG and what to read:
- 1st look at AVR lead : All waves are inverted ( all p wave, qrs complex and T wave), if it is not inverted then EKG is not right
- now calculate Heart rate ---increased or decreased??
- also check rhythm? regular or irregular??
- Now see Pwave morphology in lead 2
- next is PR interval in lead 2: noraml is 3 to 5 mm or around 3 to 4 small sq
- next is QRS complex in lead 1 and 3: look for axis deviation, normal is 2-2.5mm or < 3 small sq and qwave < 1small sq or <1/3 of R wave
- look at chest leads now : mainly qrs pattern
- ST segment: depressed or elevated
- Twave: Flat/ inverted/tall
I found this nice algorithm.....
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Approach to the ECG to assess dysrhythmias.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Common EKG findings:
http://www.skillstat.com/ecg_sim_demo.html
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Common EKG findings:
http://www.skillstat.com/ecg_sim_demo.html
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Heart Rate Calculation: 1500/ small sq between two R waves or 300/big sq between two R waves.
- when irregular HR then count R waves in 5 big sq (1 big sq = 0.2 sec so 5big sq=1 min)
- Normally there are 15 to 20 small sq between 2 R waves..
- RA hypertrophy: Tall P wave also k/s P pulmonale

- LA hypertrophy : Notched/ wide P wave , also K/s P mitrale

- both atrial Hypertrophy: Pwave will be > 2.5 small sq taller and wider..
- Axis Deviation: Check qrs wave in lead 1 and 3
LAD: left leaves
RAD: Rt reaches
- Left ventricular Hypertrophy: increase in amplitude of qRs complex wave in V1-6 but normal progression
- Right ventricular hypertrophy: increase in amplitude of QRS complex but reversal of pattern
- Strain pattern:
With LVH: Tall R waves in v5 and V6 + depressed ST segments and inverted T wave reduced in amplitude..
With RVH: in MS, Tall R waves in V1 and V2 + depressed ST segments and inverted T wave reduced in amplitude
- Biventricular hypertrophy: increase in amplitude of R wave in V1 + S wave in v2 and v1 + increase in amplitude of R wave in V5 and V6 .
- Arrythmia:
Disorder in impulse production:
- brady/Tachy
- Flutter
- Fibrillation
- Abnormal sinus rythm
- premature beats
DIsorder in Impulse conduction:
- Heart block
- WPW syndrome
- bundle branch block
- Premature Beat/ extrasystole/ ectopic beat: arise from other then SA node
If it is from Atria: then compensatory pause is incomplete but if it arise from Ventricle then compensatory pause is complete
- Supraventricular: Abnormal P wave but normal QRS complex. Lesser is the PR interval, Closer is the loci towards AV node.
- Nodal: inverted or absent P wave
- Ventricular: Absent P wave with bizarre, slurred and wide QRS complex + inverted T wave
- Sinus Pause: after pause there is Normal P wave and QRS complex and T wave but ....While in Ectopic beat abnormal pause occurs K/s Compensatory pause where abnormal P/qrs is f/b pause
>1.5 sec: Sinus arrest and next beat from other pacemakers k/s Escape beat
1.5 to 1.6 sec: from ATria
1.7: nodal/junctional
1.8 to 2.2 sec: ventricular



- Interpolated Ventricular Premature beat: Does not have any effect on sinus rhythm, means no pause but increase in PR interval of succeeding beat. Usually seen in bradycardia


- Ventricular Bigemini: when every alternate beat is VPB.

- Multifocal VPBS: when contour of VPB is different.
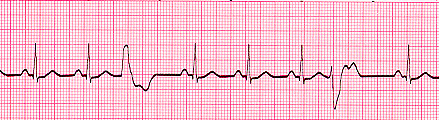
See in above ECG 3rd beat and 7th beat is premature beat(coz wide slurred QRS complex and T wave) but contour is different in both....
So in summary for premautre/ ectopic beat check both precceding and succeeding beats' P, QRS , T contour and PR interval... + contour of Premature beat
- Sinus Arrhythmia: INspiration-------------> Increase, Expiration-------------> decrease in Heart rate but normal PR interval and Normal P, QRS complex
- Sinus Bradycardia: Normal PR interval but increase R-R interval
- Sinus Tachycardia: Normal PR interval but decrease R-R interval
- Atria Rhythm: whuch includes
- Wandering pacemaker: Noramal QRS complex but contour of P wave is different so the PR interval
- ATrial Rhythm: Pwave contour and PR interval is abnormal(decreased) but constant in all beats.
- SVT: rate is usually 180 to 220 per min. While in sinus tachy is usually 120 to 180
- Atrial Flutter: Instead of P wave, there is F wave which is large, wide and multiple...Always acc/b AV block and slower ventricular Rate
- AF: p wave is not seen but Base line is finely irregular...and QRS comples comes at irregular interval....f satnds for irregular fibrillation wave which may be fine, medium or coarse(flutter-fibrillation)..each f wave occupies < 4 small sq..so atrial rate wud be >400---which is beyond A.flutter

See in this ECG contour of P wave is different: In 2nd beat , it is elevated while in 3rd beat it is inverted and so the PR interval. Showing Wandering Pacemaker...

In above ECG P wave in lead 2 is inverted which is not normal.....but it's constant and so th e PR interval....so this is Atrial Rhythm..and obviusly pacemaker is somehere in lower in Atrium...
- SVT:

Here HR= 1500/8= 187 ----------So its not sinus tachy...but SVT
here u can see P wave easily....

Here U cant see P wave but noraml QRS complex ...HR= 1500/7=214----------so SVT
Around 200 HR -------you wont be able to diff P and T wave....
- Atrial FLutter: each F wave occupies one large sq...

- Atrial fibrillation: see irregular baseline, qrs at irregular interval...and absent p wave...
