Interpretation of EKG's
Five Cardinal Features
- (1) Rate
- (2) Rhythm – including intervals
- (3) Axis
- (4) Hypertrophy
- (5) Infarction
- Three ways to determine rate:
- (1) count number of thick lines that occur between QRS complexes: 300 if next QRS on thick lines, 150 if 2nd, 100 if 3rd, then 75, 60, 50
- say: "300, 150, 100" "75, 60, 50" as counting thick lines
- can also use thin lines (thick lines bolded): 300, 250, 214, 187, 167; 150, 136, 125, 115, 107; 100, 94, 88, 83, 79; 75, 71, 68, 65, 62; 60
- (2) if bradycardic (less than 60 bpm) or irregular: count 6 second strip (2 3-second marks) and multiply by 10
- can also count entire strip (10 seconds) and multiply by 6
- (3) calculate: 1500/number of small lines between similar waves
- must determine coexisting independent rates if there are more than one
- Automaticity – heart has automaticity foci that respond at different rates and produce different morphology on EKG
- atrial – preceeded by P wave (shape of P wave changes depending upon originating focus), narrow complex QRS, normal rate 60-80/min
- junctional – no P wave, narrow QRS, normal rate 40-60/min
- ventricular – no P wave, wide QRS, normal rate 20-40/min
- Intervals
- PR should be less than 0.2 seconds (one large square)
- QRS should be less than 0.12 seconds (three small squares)
- QT interval – must be corrected for rate (QTc); in general, QT should be less than half R-R interval
- Sinus Rhythm – P before each QRS, QRS after each P, P in correct orientation (up in II)
- normal sinus rate is 60-100 bpm; if sinus rhythm but greater than 100 bpm, it is sinus tachycardia; if less than 60 bpm, it is sinus bradycardia
- Irregular Rhythms
- Sinus Arrythmia – varies with respiration, P waves identical; not pathological
- Wandering Pacemaker – irregular rhythm, P waves change shape, rate less than 100 bpm
- Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia – same as wandering pacemaker with rate greater than 100 bpm
- Atrial Fibrillation – irregular ventricular rhythm without P waves; may see erratic atrial spikes or wavy baseline
- Escape – lower level of heart will automatically respond if not driven with faster rate from above (automaticity)
- Escape Beat – single beat after a pause; can be atrial, junctional, or ventricular
- ventricular escape beats can be caused by burst of excessive parasympathetic activity (parasympathetic innervation inhibits SA node and AV junction but NOT ventricular tissue)
- Escape Rhythms – persistent escape beats (sinus node not active or not conducting); can be atrial, junctional ("idiojunctional" rhythm), or ventricular ("idioventricular" rhythm)
- idiojunctional rhythms can produce retrograde atrial depolarization with an inverted P' before, during, or after the QRS
- idioventricular rhythms caused by complete block below AV junction (P waves present but not associated with QRS) or total failure of all tissue above ventricles (downward displacement of the pacemaker)
- idioventricular rhythms can cause loss of consciousness due to insufficient cardiac output (Stokes-Adams Syndrome)
- Premature Beats – from an irritable automaticity focus; can be atrial (PAB), junctional (PJB), or ventricular (PVC; 6 PVC's per minute is pathological)
- PAB/PJB – irritable atrial and junctional foci are caused by sympathetic stimulation, caffeine, amphetamines, cocaine, digitalis, toxins, ethanol, hyperthyroidism, and stretch receptors
- PAB resets from the new P' wave at previous rate (first cycle slightly lengthened due to transient baroreceptor reflex)
- PAB's can cause wide QRS (aberrent ventricular conduction)
- PAB and PJB still depolarize the SA node (either directly or through retrograde atrial depolarization) and reset the pacing, so rhythm begins again in phase with the premature beat
- if the beat is not conducted (due to refractoriness), the missed QRS in produces a long empty baseline (harmless)
- can occur every other beat (atrial or junctional bigeminy) or every third beat (atrial or junctional trigeminy)
- PVC – irritable ventricular foci are caused by low oxygen, hypokalemia, or muscle pathology (mitral valve prolapse, myocarditis, etc.)
- PVC's do not depolarize the SA node, so there is a "compensatory" pause after them (except for "interpolated" PVC's, where they occur exactly where the ventricular contraction would have)
- P waves continue unaffected and the next QRS occurs where it would have if there had been no PVC
- a PVC that falls on a T wave ("R on T phenomenon") can cause sustained ventricular tachycardia
- ventricular parasystole – ventricular tissue with entrance block (NOT an irritable focus) that starts PVC's at its own automatic firing rate
- Tachyarrhythmias
- Paroxysmal tachycardia – 150-250 bpm; can be atrial (PAT), junctional (PJT), or ventricular (PVT)
- atrial (PAT) or junctional (PJT) are also called paroxysmal superventricular tachycardia (PSVT)
- paroxysmal atrial tachycardia with block (PAT with more than one P wave before each QRS) – caused by digitalis
- AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) is a type of PJT
- PJT may still have retrograde atrial depolarization and inverted P' waves
- PJT may involve somewhat widened QRS since one bundle branch may still be refractory when next beat arrives (aberrent ventricular conduction)
- PVT:
- during PVT, if the P wave appears at just the right time, can see normal QRS (capture beat) or QRS that degenerates into a PVC (fusion beat)
- PVT can be distinguished from PSVT with wide QRS (caused by BBB, etc.) by the following:
- presence of coronary artery disease
- very wide QRS (more than 0.14 sec)
- extreme RAD
- AV dissociation (see capture or fusion beats)
- Torsades des Pointes – "party streamer"; caused by two competitive, irritable foci in different ventricular areas
- Flutter – 250-350 bpm; can be atrial (sawtooth baseline with QRS's) or ventricular (sine wave; almost always leads to fibrillation unless treated)
- Fibrillation – greater than 350 bpm; can be atrial (jagged baseline with QRS's) or ventricular (no identifiable waves)
- no pumping occurs
- atrial fibrillation can produce a narrow-complex tachycardia (rapid ventricular response)
- Block – identify by pauses (sinus block), abnormal PR intervals (AV blocks), abnormal QRS interval (bundle branch block), or axis deviation (hemiblock)
- Sinus Block – spontaneous pause in electrical activity; can restart automatically or have an escape beat (see above)
- AV Block – causes abnormal PR interval
- 1st degree block – PR too long (greater than 0.2 seconds, or one large square)
- 2nd degree block – some P waves without QRS:
- Wenkebach (Mobitz I) – block at the node itself; PR gradually lengthens until a P does not produce a QRS
- Mobitz II – block beyond the node; PR length constant, but some P waves do not produce QRS (can be 2:1, 3:1, etc., or even intermittent)
- 2:1 block can be either of above; can use vagal maneuvers to differentiate (see below)
- 3rd degree block – none of the P waves get through; there is an idioventricular or idiojunctional rate instead
- Bundle Brach Block – basically two out of phase QRS's (R R'); requires wide QRS for diagnosis (at least 3 small squares; best to use limb leads since low voltages allow for more accurate measurement)
- Right Bundle Branch Block (RBBB) – QRS has two peaks (R R') in V1 or V2 usually returning to lower than baseline between them
- Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) – QRS has two peaks (R R') in V5 or V6 with slight depression between them
- BBB makes ventricular hypertrophy criteria unreliable
- LBBB makes infarction difficult to determine
- BBB can cause SVT to degenerate more easily into VT
- Hemiblock – block of anterior or posterior fascicle of LBB; causes axis deviation and widened QRS
- Anterior hemiblock – left axis deviation with a Q wave in I and a prominent S wave in III
- Posterior hemiblock – right axis deviation with a prominent S wave in I and a Q wave in III
- can have bifascicular blocks (RBBB + hemiblock)
- must have previous EKG to diagnose so that other causes of axis deviation can be ruled out
- Vagal Maneuvers (gagging or carotid sinus massage) – inhibit irritable atrial or junctional foci or increase the refractoriness of the AV node
- abolishes PSVT, identifies 2:1 AV block (no effect if Mobitz II), and reveals flutter waves in atrial flutter
- find axis quadrant using below diagram (QRS above or below baseline in each lead):
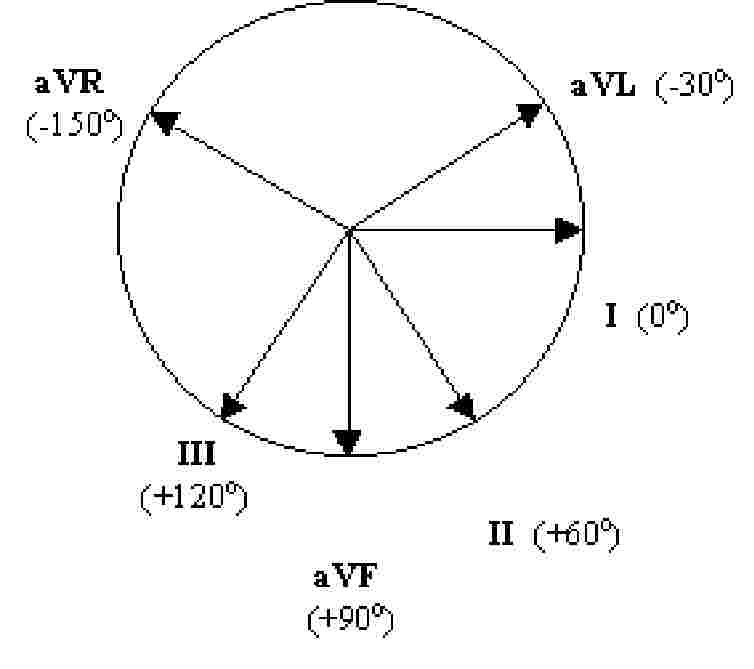
- axis is also 90 degrees from isoelectric QRS (same up as down) or in the direction of a QRS that only goes up (opposite direction of QRS that only goes down)
- Normal axis is "up in I and aVF" (some say "up in I and II")
- if I is down: right axis deviation (RAD)
- if aVF is down: left axis deviation (LAD)
- if both are down: extreme RAD
- Axis Rotation – find isoelectric QRS (same up as down) in chest leads (V1 to V6); normally occurs in V3 or V4
- if isoelectric in V1 or V2: rightward rotation
- if isoelectric in V5 or V6: leftward rotation
- Atrial Hypertrophy – diphasic P wave in V1
- right atrial hypertrophy – large initial component of diphasic P wave in V1
- left atrial hypertrophy – large terminal component of diphasic P wave in V1
- Ventricular Hypertrophy – tall R wave in V1 for RVH, deep S wave in V1 and tall R wave in V5 for LVH
- right ventricular hypertrophy – widened QRS with RAD, rightward rotation, and:
- R greater than S in V1 but R gets smaller in V2 through V6
- S wave persists in V5 and V6
- left ventricular hypertrophy – widened QRS with LAD, leftward rotation, and:
- sum of depth of S in V1 and height of R in V5 is more than 35 small squares
- inverted T wave with gradual downslope and rapid upslope
Infarction – always requires previous EKG for comparison
- Identifying Injury
- (1) ischemia – inverted T waves (earliest sign) – symmetrical down- and upslope, opposite direction of QRS
- (2) acute injury – ST elevation
- can occur without Q waves: "non Q-wave MI"
- ST depression may indicate "subendocardial infarction" (small shallow area as opposed to entire wall of heart)
- (3) necrosis (non-conductive tissue) – Q-waves
- significant if more than one small square wide or greater than 1/3 the amplitude of the QRS
- remain even after acute infarction is over (unlike other two)
- Localizing Injury – leads where the above occur; also remember that axis points away from infarction
- Anterior – left anterior descending artery – V1 to V4
- Lateral – circumflex artery – I, aVL
- Inferior – right or left coronary artery – II, III, aVF
- Posterior – right coronary artery – V1 and V2, but changes are mirror image (R instead of Q, ST depression instead of elevation, etc.)
- for blocks and hemiblocks: AV node is supplied by the right coronary artery, RBB and anterior LBB is supplied by LAD, posterior LBB is supplied by either
- Pulmonary Embolism
- prominent S wave in I
- Q wave in III
- inverted T waves in III and V1 through V4
- ST depression in II
- acute incomplete RBBB
- RAD with rightward rotation
- Electrolyte Disturbances
- hyperkalemia
- wide flat P – P disappears entirely with severe hyperkalemia
- wide QRS
- peaked T wave
- hypokalemia
- flat T wave
- U wave (after T wave; represents Purkinje cell repolarization) – prominent with severe hypokalemia
- can cause torsades des pointes if extreme
- hypercalcemia – shortened QT interval
- hypocalcemia – prolonged QT interval
- Drugs
- Digitalis
- therapeutic – ST slopes below baseline, inverted T waves, shortened QT
- excessive – blocks: SA block, paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) with block, AV block (can be 3rd degree)
- toxic – atrial fibrillation, junctional or ventricular tachycardia, frequent PVC's, ventricular fibrillation
- Quinidine (blocks potassium channels)
- wide notched P wave
- wide QRS
- very deep ST
- U wave
- long QT interval
- Pericarditis
- flat or concave downward ST segment elevation in leads where QRS is mainly negative (right chest leads – V1 to V3)
- elevated ST segment with T wave off baseline in leads where QRS is mainly positive (lateral/inferior limb leads – aVL, I, II, aVF, III)
- COPD
- all waves of minimal amplitude; often leads to RVH with RAD; MAT in some cases
- Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome – caused by accessory bundle of Kent that bypasses the AV node to allow ventricular pre-excitation
- delta wave with apparently shortened PR interval
- can cause tachycardia through three mechanisms:
- (1) rapid conduction of rapid atrial beats (PSVT, atrial flutter, or atrial fibrillation)
- (2) automaticity foci within the bundle
- (3) re-entry of ventricular depolarization
- Lown-Ganong-Levine Syndrome – caused by James bundle (extention of the anterior internodal tract) that bypasses the AV node directly to the bundle of His
- no PR delay (so PR interval is minimal)
- QRS immediately responds to any atrial tachyarrythmias, so (for example) atrial flutter produces a rapid QRS response
- Brugada Syndrome – familial dysfunction of Na+ channels
- characterized by RBBB with ST elevation (downsloping) in V1 through V3
- can cause deadly arrythmias leading to sudden cardiac death with no apparent structural heart disease (responsible for half of all cases)
- Wellen's Syndrome – stenosis of LAD
- causes marked T-wave inversion in V2 and V3
- Long QT Syndrome – QT interval more than 1/2 the cardiac cycle
- predisposed to ventricular arrythmias
No comments:
Post a Comment